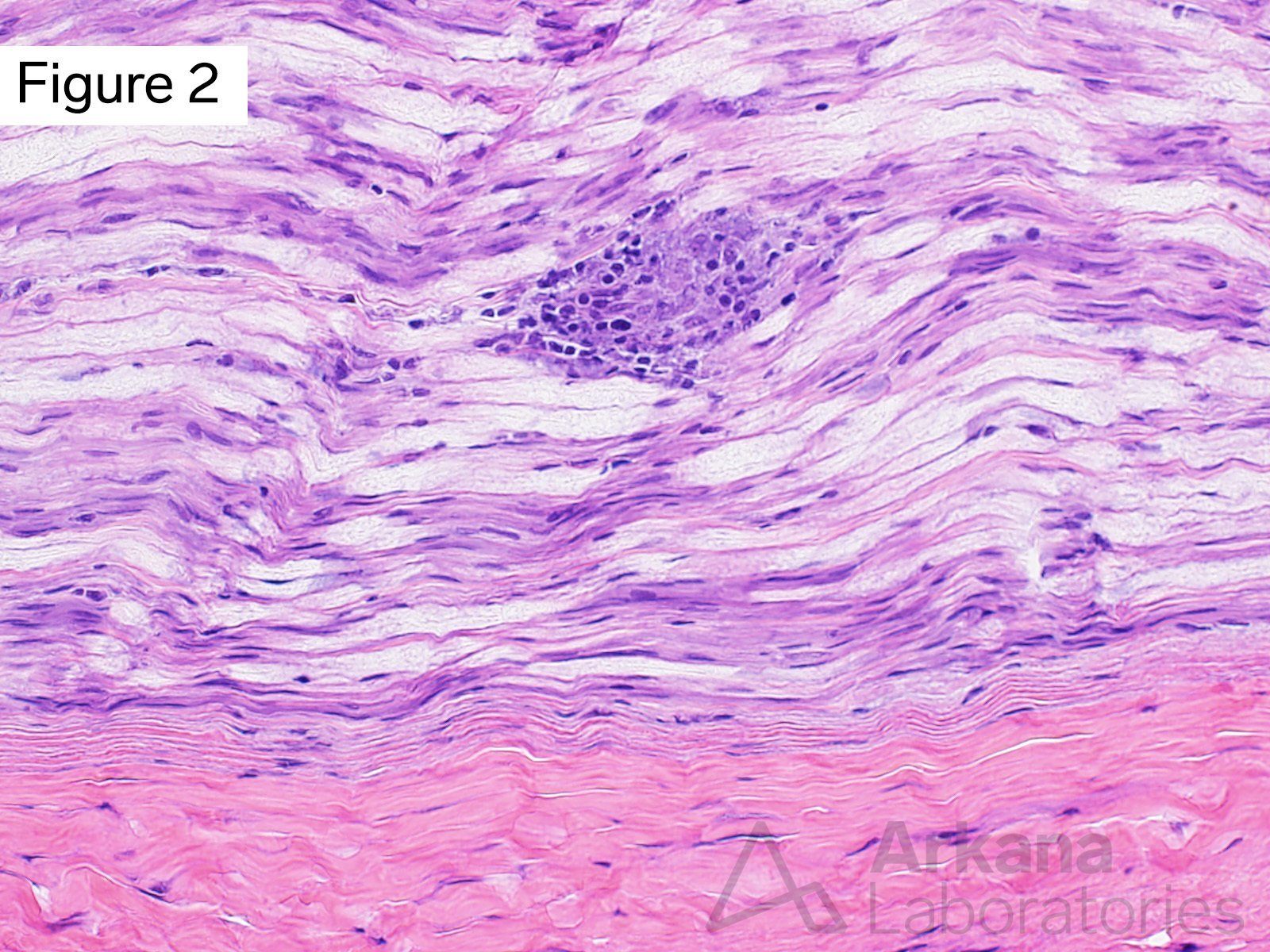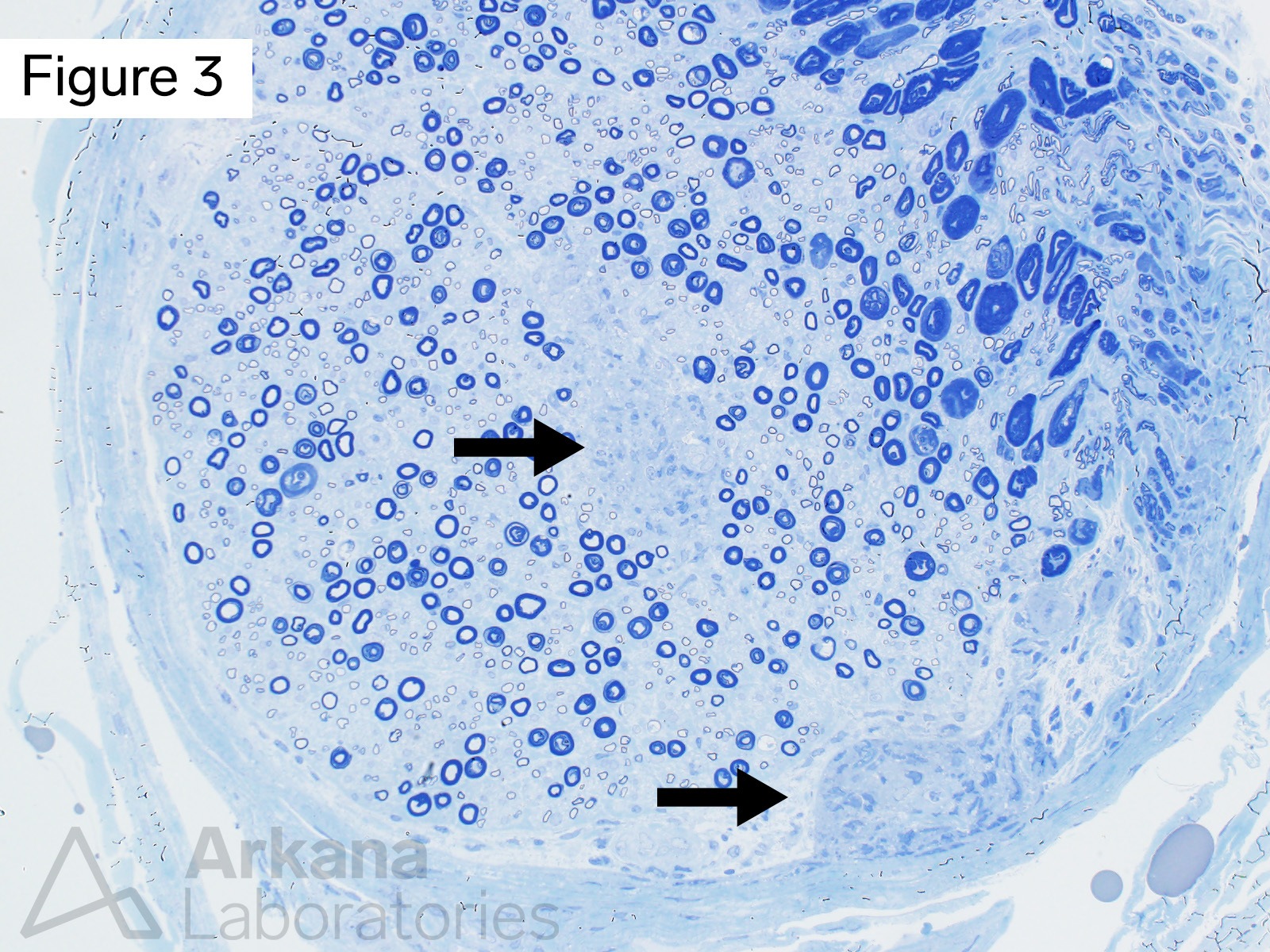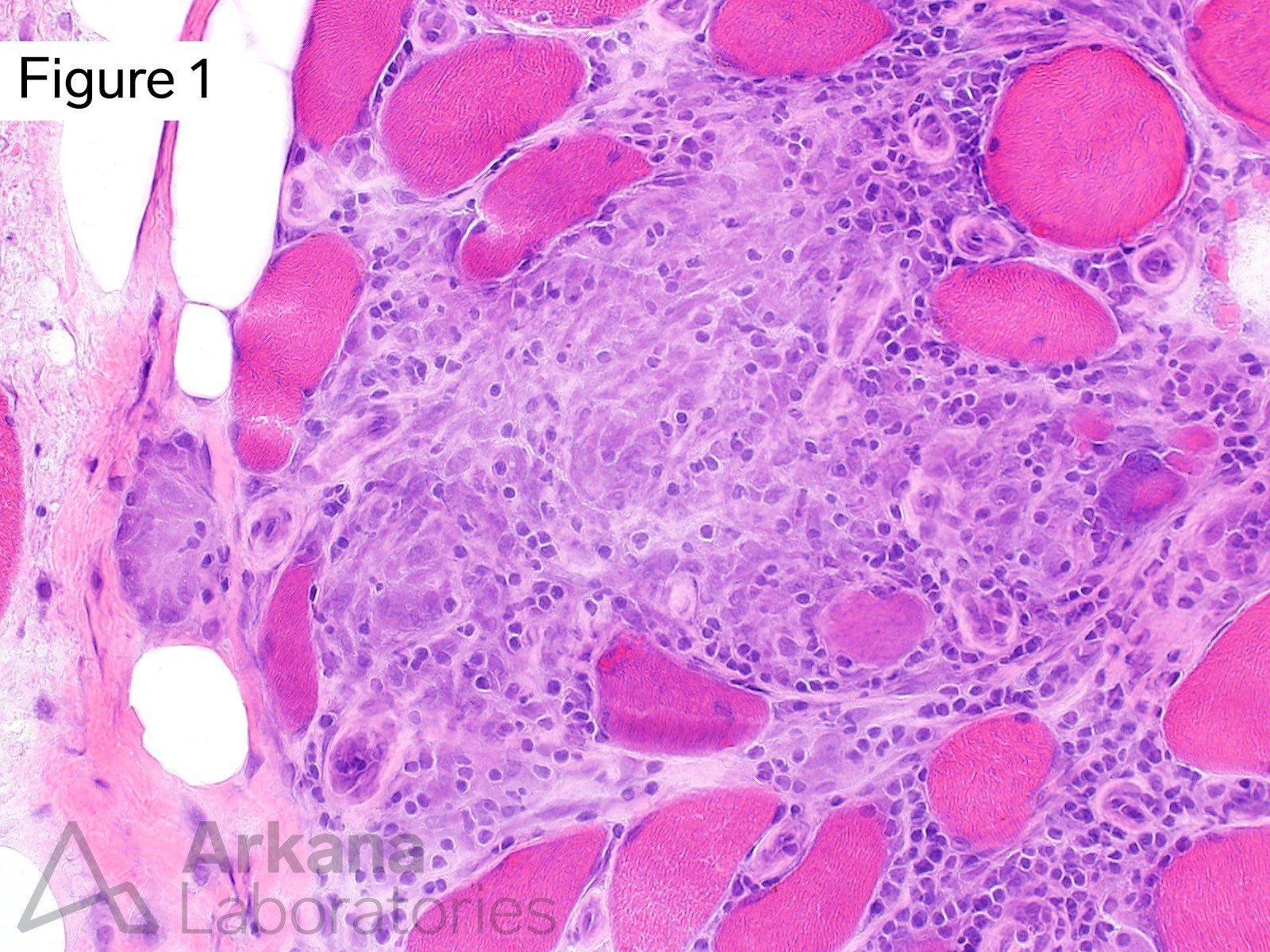
This 40-year-old patient presented with a three year history of slowly progressive generalized muscle weakness. More recently their hands and feet developed numbness and tingling. Chest CT showed bilateral hilar adenopathy. Electrodiagnostic studies (EMG/NCS) showed features of a predominantly axonopathic sensorimotor neuropathy as well as features of myopathic process. On physical examination atrophy of intrinsic hand muscles was noted.
Which of the following abnormalities is seen in Figures 1 – 3?
A. Vasculitis
B. Granulomata
C. Amyloid
D. Acute abscess
Correct Answer: Granulomata
Figures #1 – #3 show focal collections of noncaseating granulomata involving skeletal muscle and peripheral nerve. The morphologic features are consistent with the presence of granulomatous myopathy and neuropathy (neuromyopathy). Special stains for acid fast bacilli and fungi were negative. Transbronchial biopsy showed granulomata within the perihilar lymph nodes. These finding are most compatible with the diagnosis of sarcoidosis. However, clinical correlation is required as sarcoidosis is a diagnosis of exclusion.
Sarcoidosis is a multisystemic disorder of uncertain etiology. Extrapulmonary disease may involve many sites, including neurosarcoidosis (brain, spinal cord, dura), skeletal muscle and peripheral nerve. Interestingly, patient’s with sarcoidosis may develop small fiber neuropathy.
Reference(s)/additional reading
Katie Bechman, Dimitrios Christidis, Sarah Walsh, Surinder S Birring, James Galloway, A review of the musculoskeletal manifestations of sarcoidosis, Rheumatology, Volume 57, Issue 5, May 2018, Pages 777–783, https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kex317
Challenor YB, Felton CP, Brust JC. Peripheral nerve involvement in sarcoidosis: an electrodiagnostic study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 Nov;47(11):1219-22. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.11.1219. PMID: 6094734; PMCID: PMC1028090.
Valeyre D, Jeny F, Rotenberg C, Bouvry D, Uzunhan Y, Sève P, Nunes H, Bernaudin JF. How to Tackle the Diagnosis and Treatment in the Diverse Scenarios of Extrapulmonary Sarcoidosis. Adv Ther. 2021 Sep;38(9):4605-4627. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01832-5. Epub 2021 Jul 22. PMID: 34296400; PMCID: PMC8408061.
Challenor YB, Felton CP, Brust JC. Peripheral nerve involvement in sarcoidosis: an electrodiagnostic study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 Nov;47(11):1219-22. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.11.1219. PMID: 6094734; PMCID: PMC1028090.
Voortman M, Hendriks CMR, Elfferich MDP, Bonella F, Møller J, De Vries J, Costabel U, Drent M. The Burden of Sarcoidosis Symptoms from a Patient Perspective. Lung. 2019 Apr;197(2):155-161. doi: 10.1007/s00408-019-00206-7. Epub 2019 Feb 16. Erratum in: Lung. 2019 Apr 8;: PMID: 30778661; PMCID: PMC6486948.
Quick note: This post is to be used for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical or health advice. Each person should consult their own doctor with respect to matters referenced. Arkana Laboratories assumes no liability for actions taken in reliance upon the information contained herein.