The image above shows myelinosomes, also known as “zebra bodies” for their appearance on tangential sectioning. Myelinosomes are seen in Fabry disease, a rare x-linked recessive genetic disorder caused by the defective activity of the enzyme alpha-galactosidase A. Renal, cardiac, and cerebrovascular involvement is common and can be fatal by the 4th decade without enzyme replacement therapy.
Alpha galactosidase A deficiency results in accumulation of globotriaosylceramide within podocytes of glomeruli, tubules, myocytes, and endothelium. Globotriaosylceramide accumulation results in the formation of myelinosomes. Since myelinosomes are lipid-derived, they are maintained on osmium fixation, but are lost with exposure to xylenes in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. While characteristic, this finding is not pathognomonic of Fabry’s disease and can also be seen with the use of cationic and lipophilic medications. Myelinosome formation is related to drug toxicity of chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, amiodarone, gentamicin, ranolazine, and others (See references below).
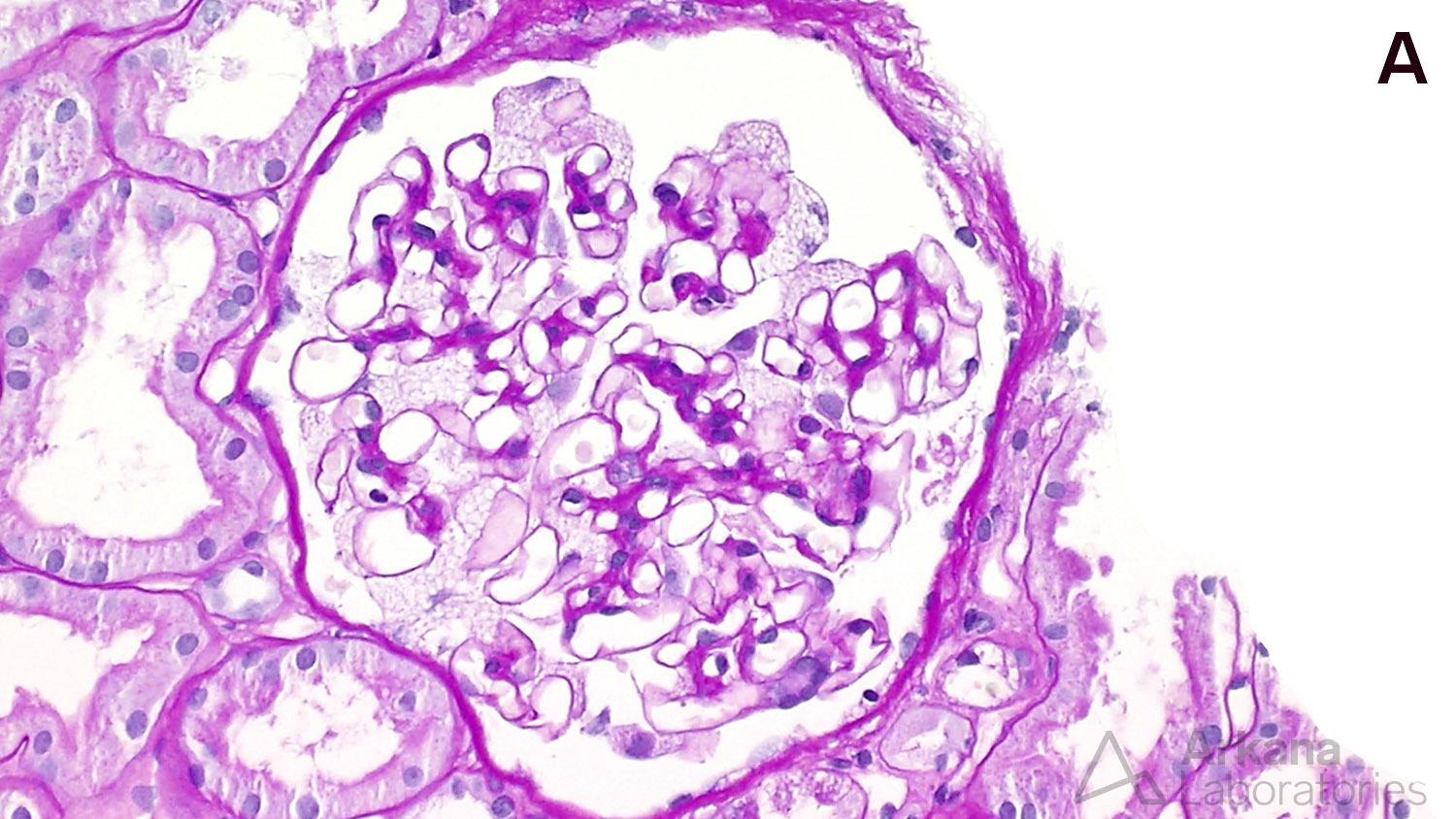
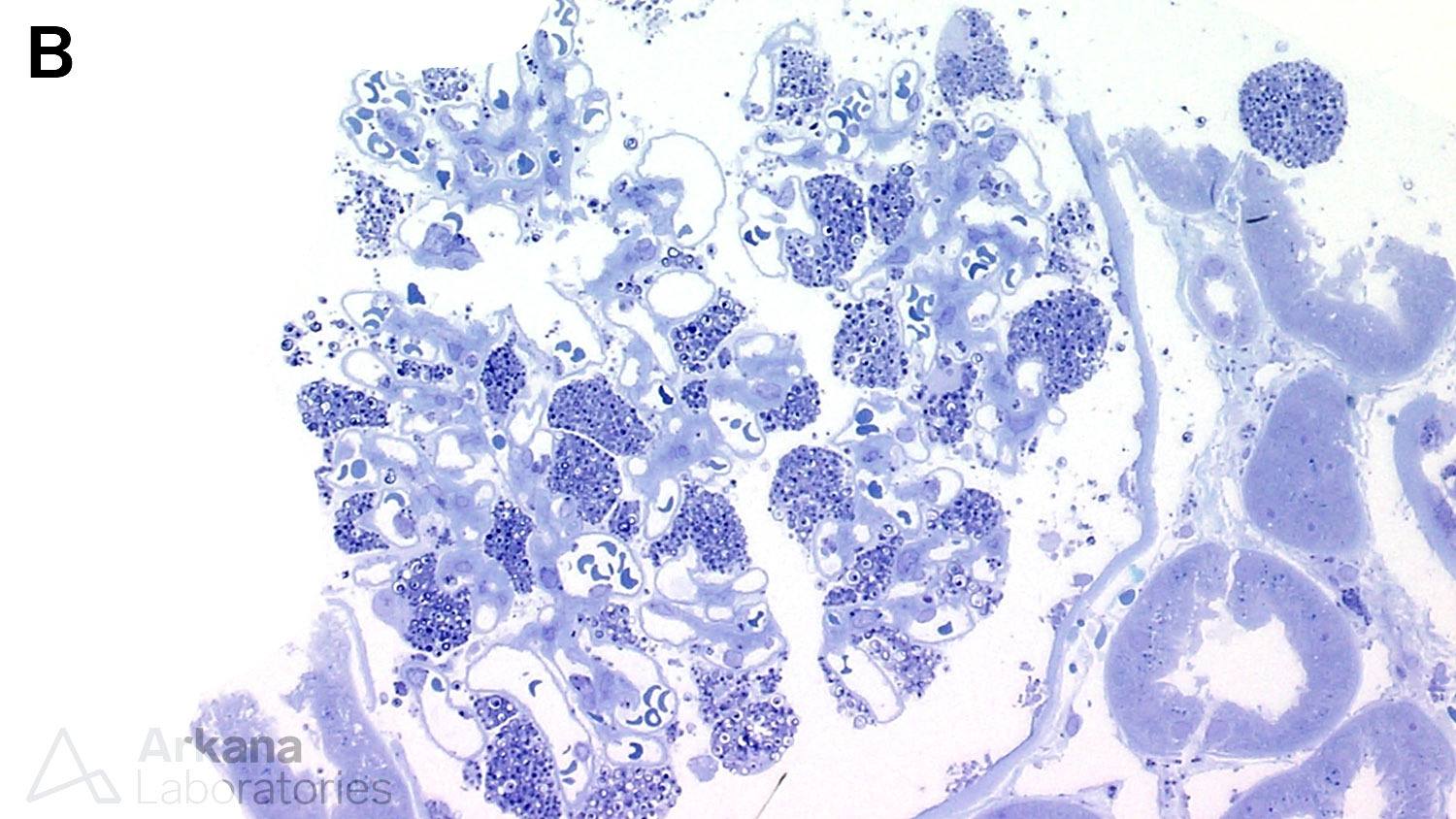
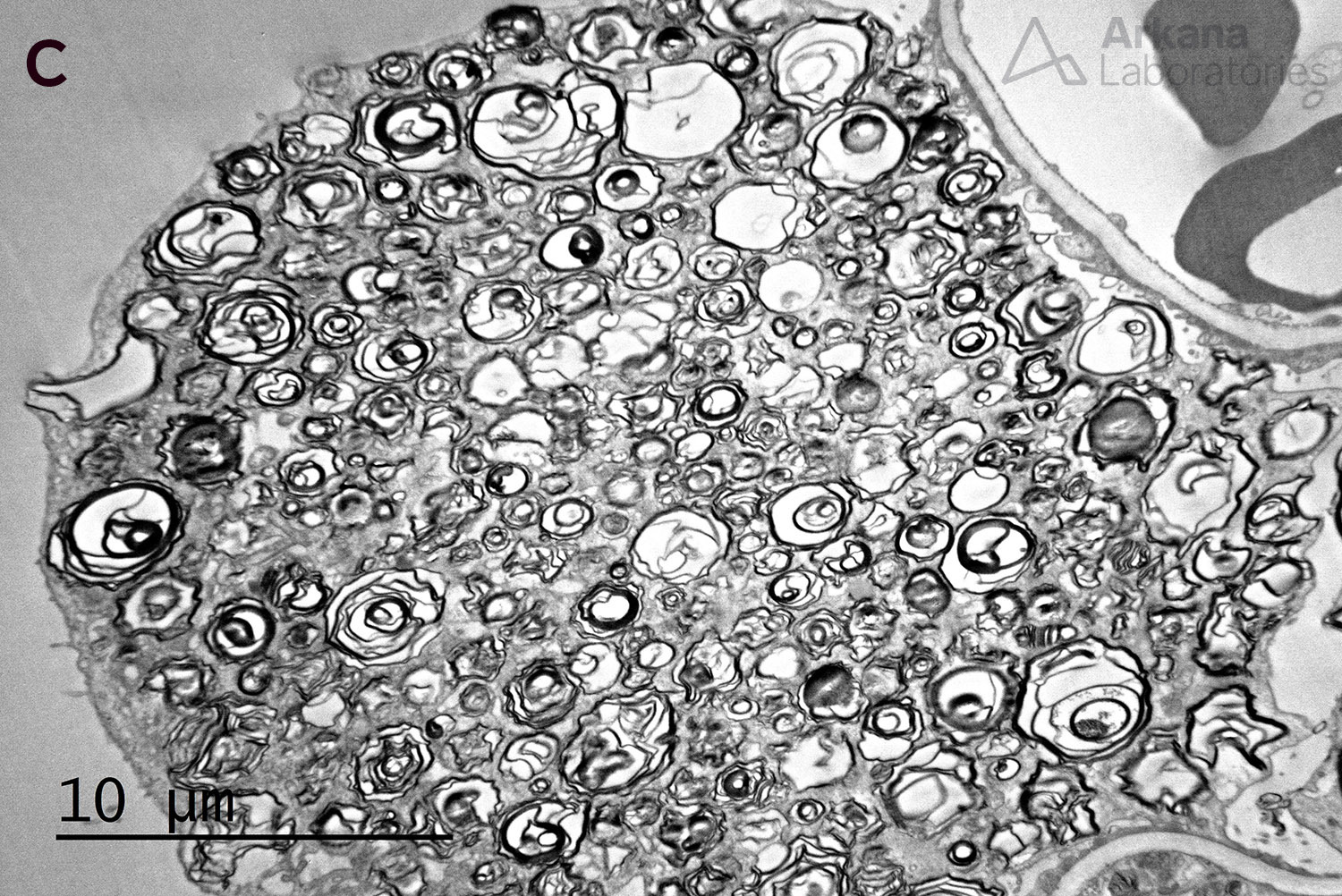
Below is a renal biopsy from a patient with Fabry disease showing enlarged podocytes with a bubbly, vacuolated appearance on PAS stain, corresponding to the negative image of myelinosomes (A). These show the formation of dense structures on toluidine blue stained sections (B). On electron microscopy, there are numerous myelinosomes are identified within podocytes (C). Another finding that can occur on renal biopsies of patients of Fabry disease is focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (not shown).
In less severe cases where fewer myelinosomes are identified, consider secondary causes, much as the medications listed above. Fabry disease can be ruled out in such cases by measuring alpha-galactosidase A activity in serum or urine samples.
References:
Halliwell WH. Cationic amphiphilic drug-induced phospholipidosis. Toxicol Pathol 1996; 25 (1): 53-60.
Muller-Hocker J, Schmid H, Weiss M, Dendorfer U, Braun GS. Chloroquine-induced phospholipidosis of the kidney mimicking Fabry’s disease: case report and review of the literature. Human Pathology 2003 March; 34 (3): 285-289.
de Menezes Neves P, Machado JR, Custodio FB, Goncalves dos Reis Monteiro ML, Iwamoto S, Freire M, Ferreira MF, Antonia dos Reis M. Ultrastructural deposits appearing as “zebra bodies” in renal biopsy: Fabry disease? – comparative case reports. BMC Nephrology 2017; 18:157.
Scheurle C, Dammrich M, Baumgartel MW. Renal phospholipidosis possibly induced by ranolazine. Clinical Kidney Journal 2014; 7: 62-64.
Quick note: This post is to be used for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical or health advice. Each person should consult their own doctor with respect to matters referenced. Arkana Laboratories assumes no liability for actions taken in reliance upon the information contained herein.