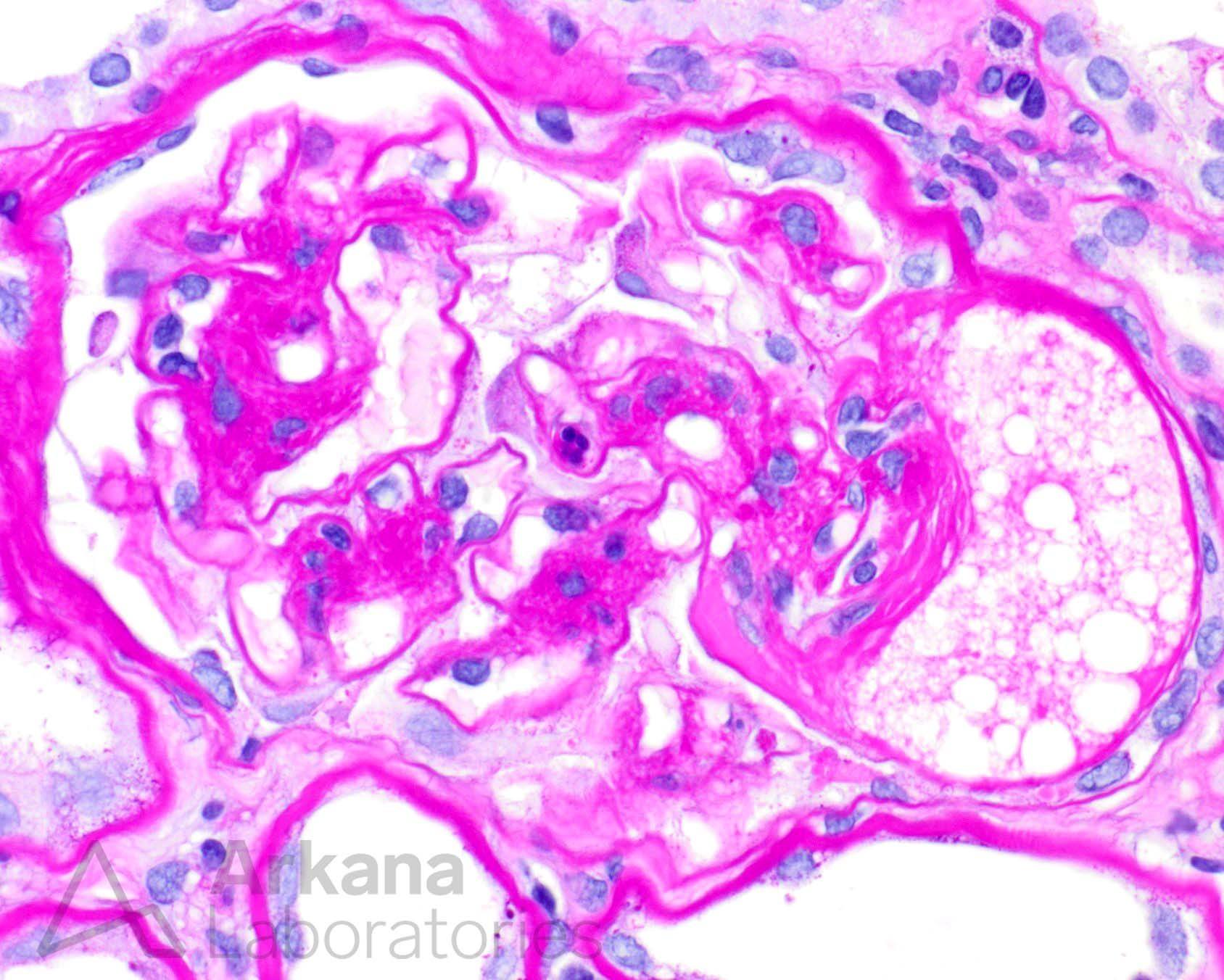
Which underlying systemic disease does this patient most likely have?
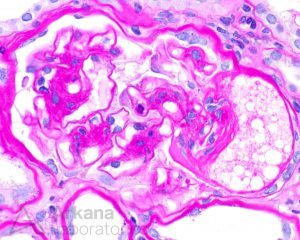
The biopsy shows mesangial matrix expansion and a capillary microaneurysms. These findings are typically seen in the setting of diabetes, in which mesangial matrix expansion and mesangiolysis lead to loss of capillary wall attachments and microaneurysmal dilatation. In this case, there is lipid within the microaneurysm, likely within an endothelial “foam” cell in an area of early segmental sclerosis. The differential diagnosis includes idiopathic nodular glomerulosclerosis, which may be seen in association with hypertension and/or smoking.
Quick note: This post is to be used for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical or health advice. Each person should consult their own doctor with respect to matters referenced. Arkana Laboratories assumes no liability for actions taken in reliance upon the information contained herein.