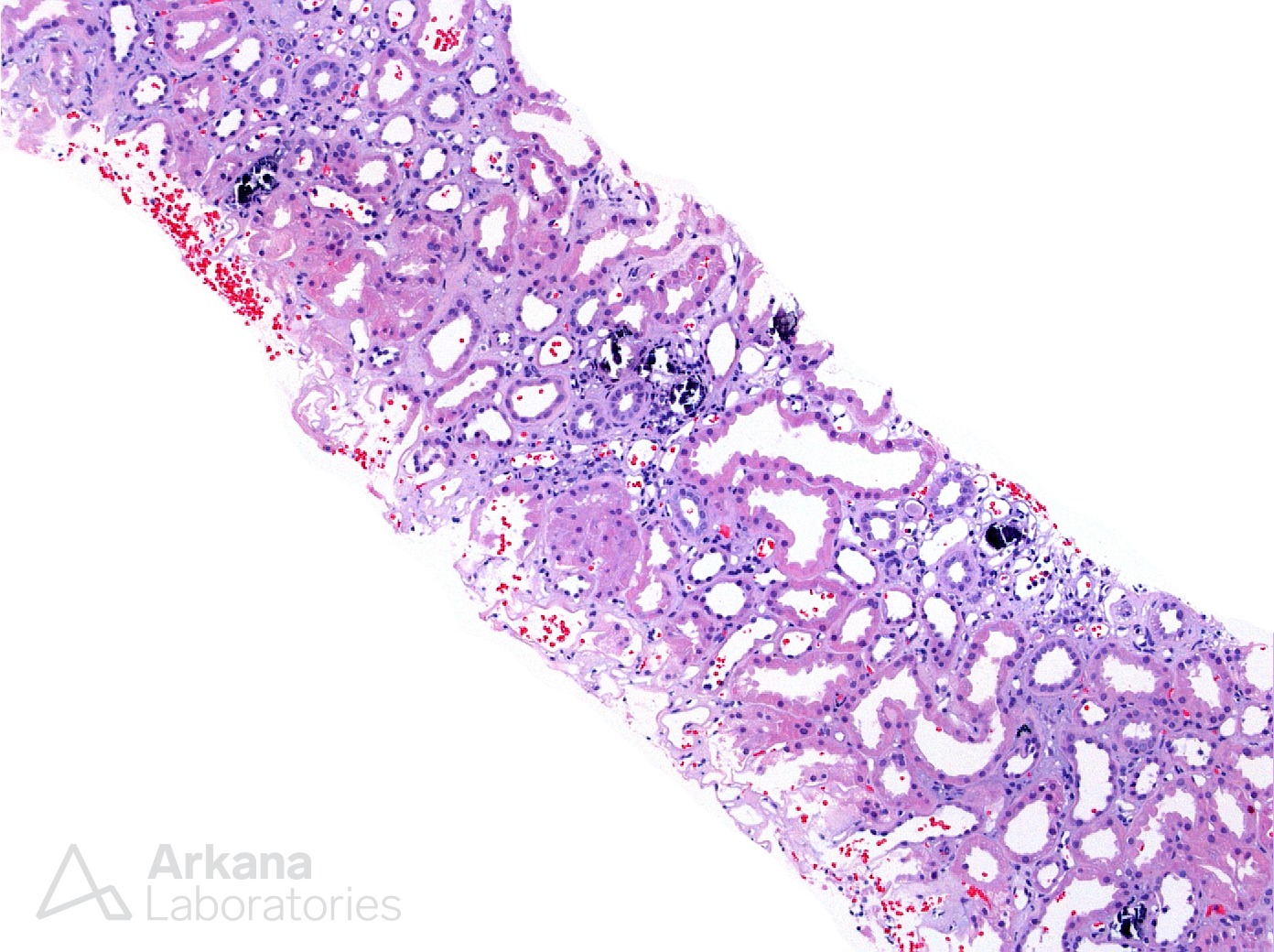
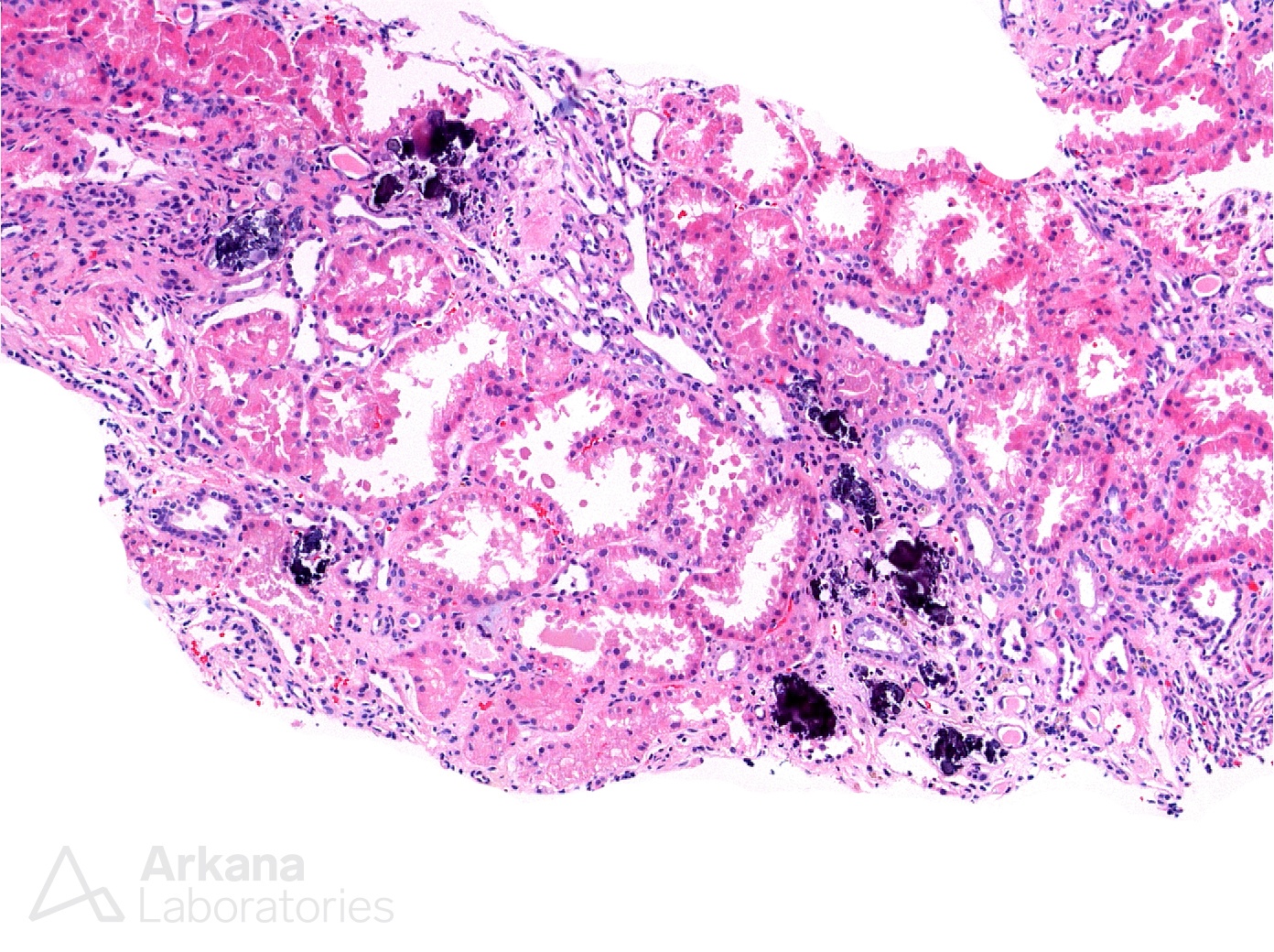
The renal biopsy in these photomicrographs shows tubular injury with increased interstitial calcium phosphate deposition. Focal interstitial calcium phosphate can be a nonspecific finding in the setting of acute tubular injury. However, the degree of deposition present in this biopsy is likely to be the pathologic driver of the kidney injury. The differential diagnosis would include nephrocalcinosis related to hypercalcemic conditions versus acute phosphate nephropathy secondary to exposure to high doses of phosphorus. Nephrocalcinosis can occur in hypercalcemic conditions of any cause including sarcoidosis, milk-alkali syndrome, excessive vitamin D therapy, primary hyperparathyroidism, malignancy, and inherited tubulopathies such as Dent disease.
Quick note: This post is to be used for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical or health advice. Each person should consult their own doctor with respect to matters referenced. Arkana Laboratories assumes no liability for actions taken in reliance upon the information contained herein.