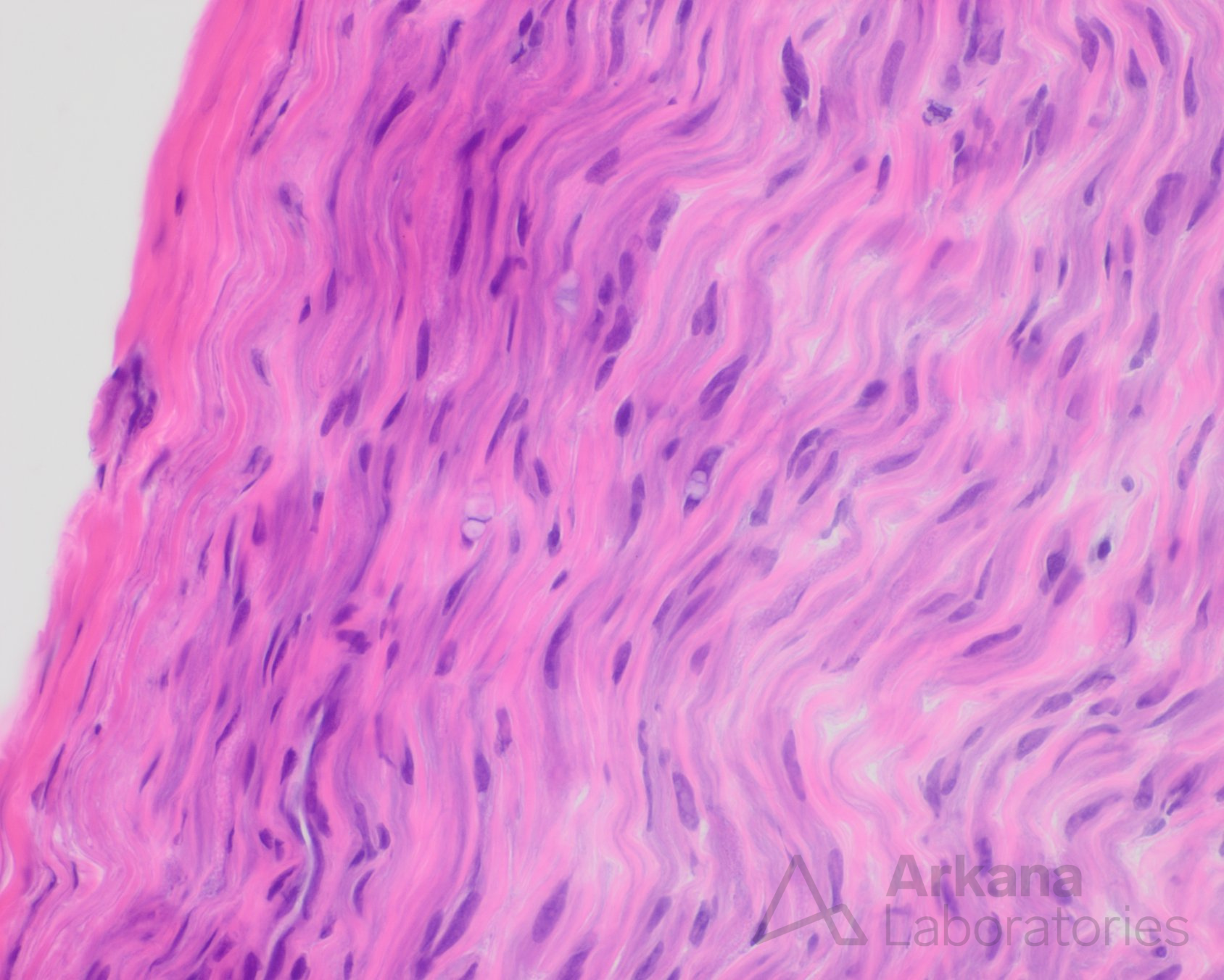
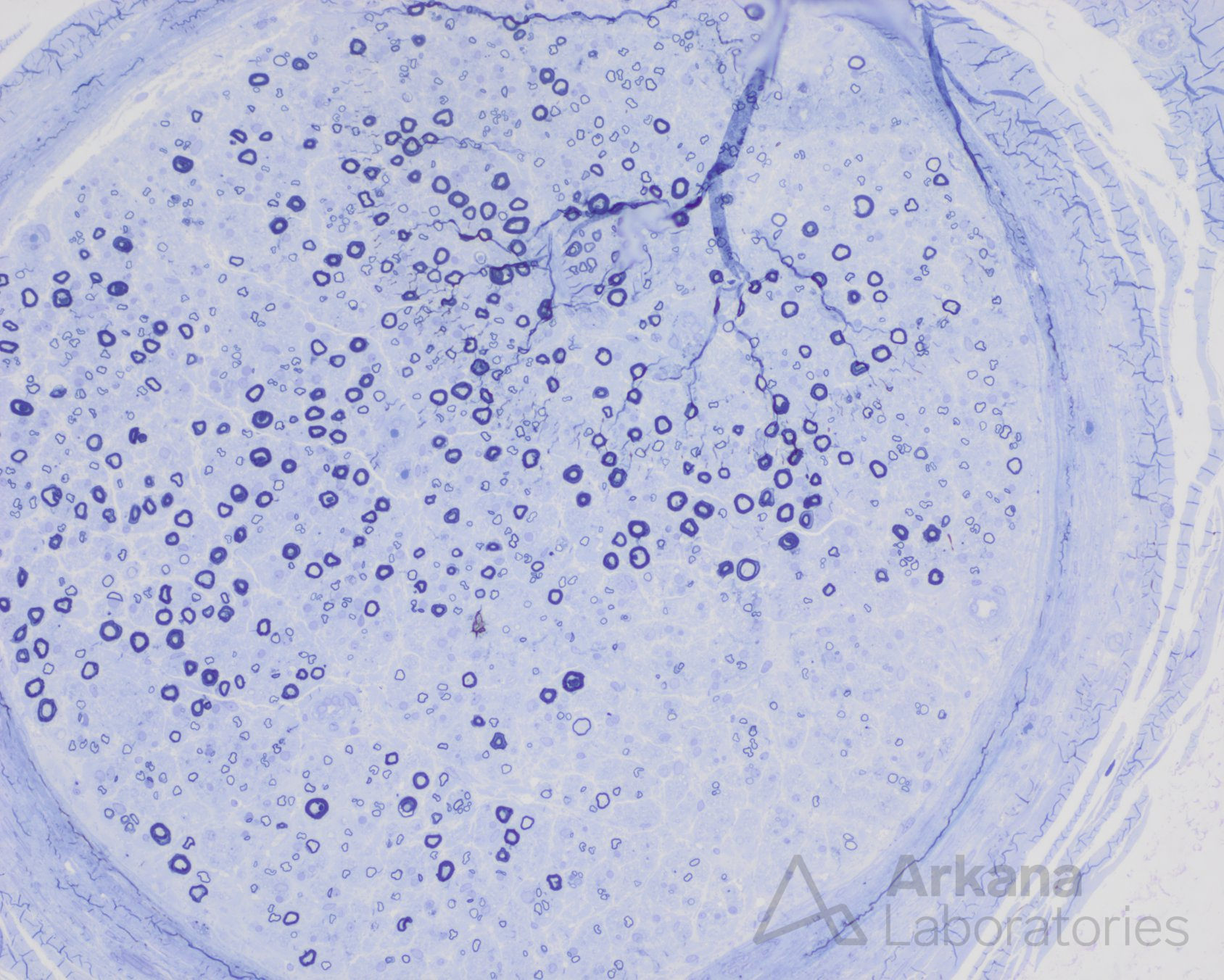
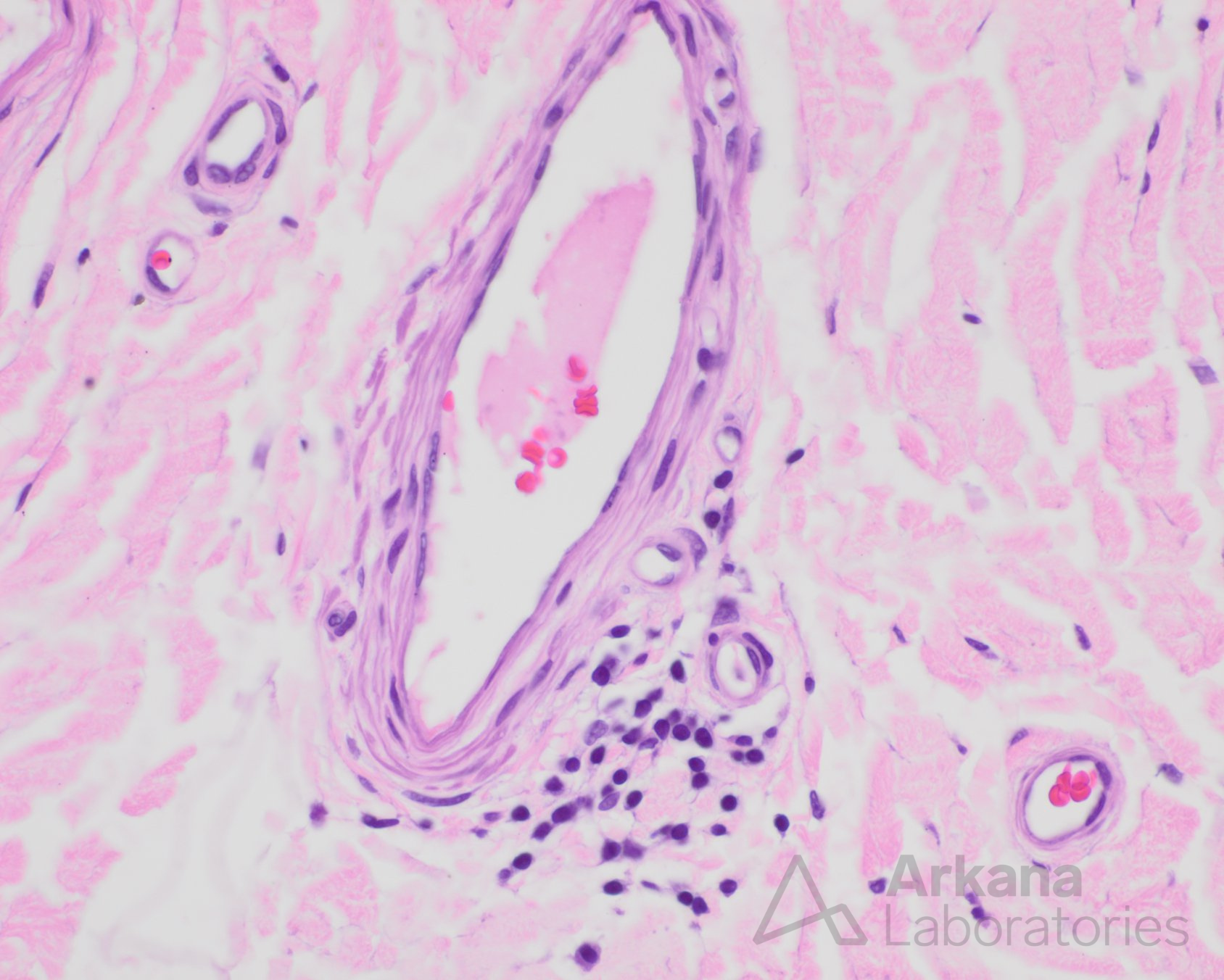
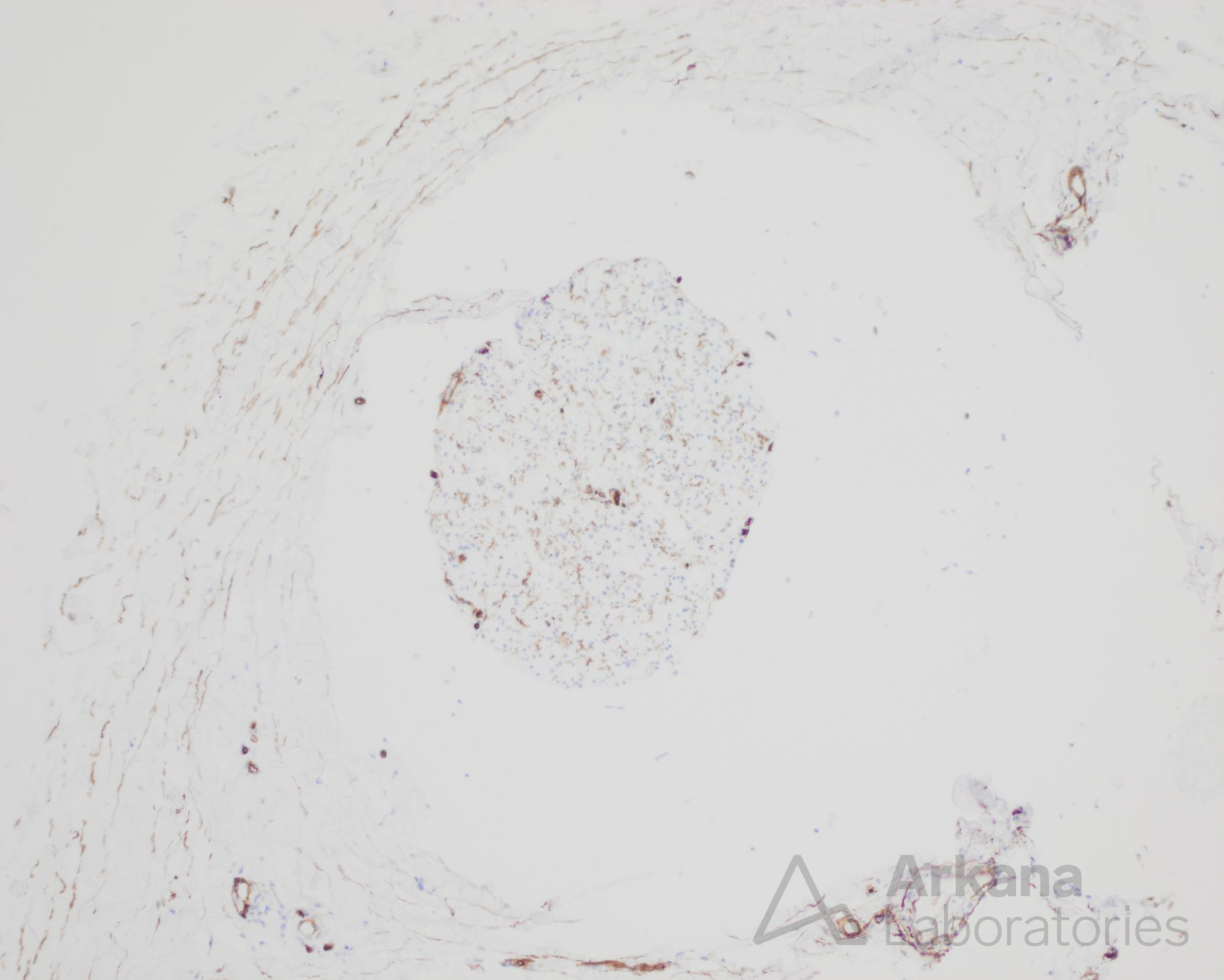
Clinical History
The patient is a 62-year-old man with sudden onset of progressive anesthesia and dysesthesia in hands & feet, and left foot drop. His current medications are atorvastatin, gabapentin, levothyroxine and pregabalin. His past medical history is remarkable for Sjögren’s syndrome. At the time of biopsy his diagnosis is sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy.
What pathology is missing from this picture?
A. Thinly myelinated segments
B. IgG deposition
C. Fibrinoid necrosis
D. Onion bulbs
Correct Answer: C. Fibrinoid necrosis
Final Diagnoses:
-Zonal axonopathy, active
-Perivascular lymphocytic inflammation
-Findings suspicious for vasculitis
Fibrinoid necrosis / mural wall injury is missing for the diagnosis of definite vasculitic neuropathy
However, the presence of zonal axonopathy, active axonal degeneration and perivascular inflammation are sufficient for “probable” vasculitic neuropathy based on Peripheral Nerve Society international guidelines
These expert-consensus guidelines have not been independently evaluated and treatment decisions should include clinical correlation.
Reference(s) / additional reading:
- Chkheidze R, Pytel, P. JNEN. 2020;79(4):355-364.
- Collins MP, Hadden RD. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017;13(5):302-316.
- Collins MP, Kissel JT, et al. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2010;15(3):176-84.
Quick note: This post is to be used for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical or health advice. Each person should consult their own doctor with respect to matters referenced. Arkana Laboratories assumes no liability for actions taken in reliance upon the information contained herein.