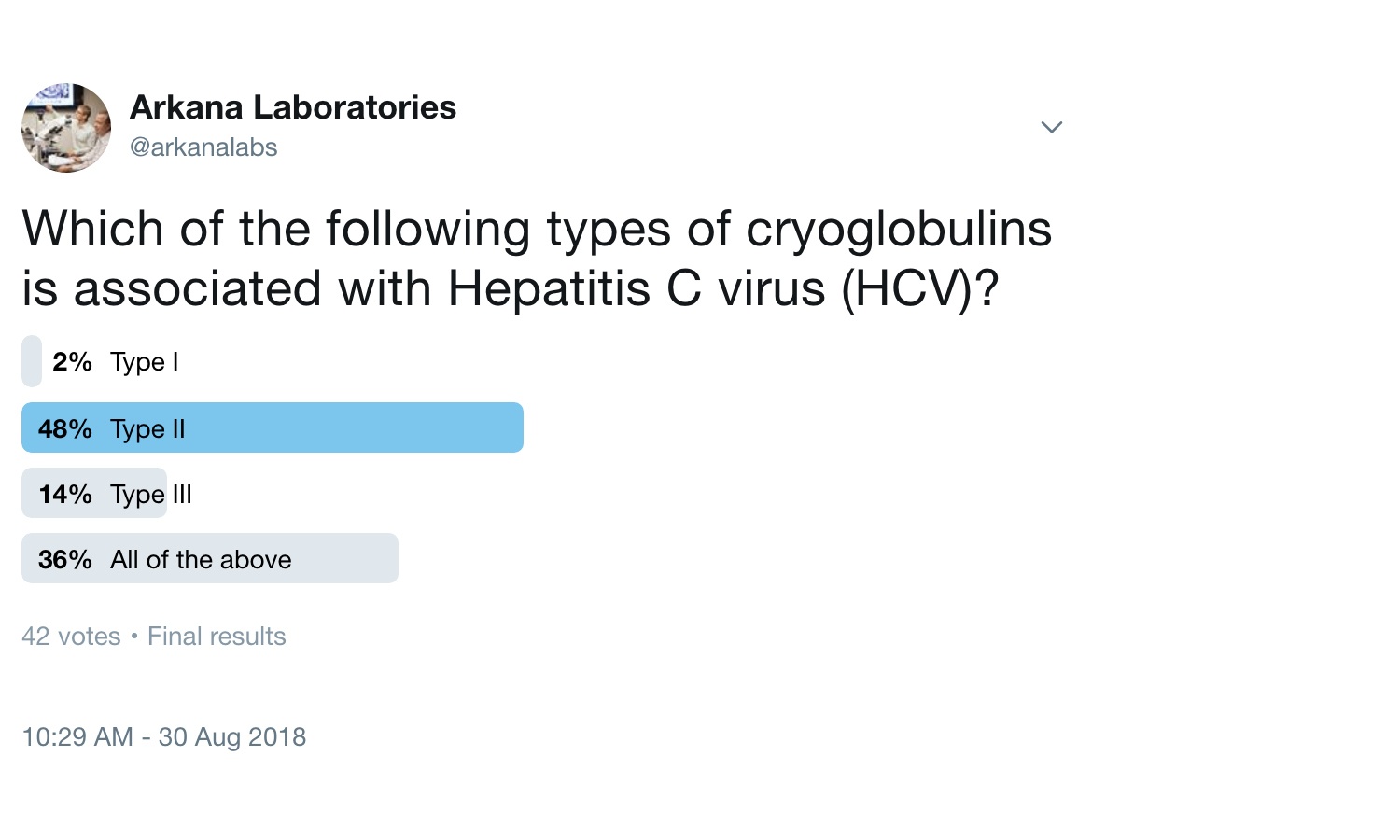
ANSWER: B
Type II (mixed) cryoglobulinemia is characterized by immune-complexes containing a monoclonal Ig (usually IgM) that have an RF activity and polyclonal Ig (usually IgG). It’s most commonly caused by HCV, with some cases caused by lymphoproliferative or autoimmune disorders.
References:
Zaidan M, et al. Spectrum and prognosis of noninfectious renal mixed cryoglobulinemic GN. J Am Soc Nephrol 2016; 27:1-12.
Fabrizi F, et al. Hepatitis C virus infection, mixed cryoglobulinemia, and kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis 2013; 61(4): 623-637.
Quick note: This post is to be used for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical or health advice. Each person should consult their own doctor with respect to matters referenced. Arkana Laboratories assumes no liability for actions taken in reliance upon the information contained herein.